The event log consolidation and process tracking tables might grow too large after a while. You can configure your system to periodically purge records that are no longer of interest, e.g. after 3 months. The following examples show how this can be done on MS SQL Server 2000 and MySQL.
Microsoft SQL Server
| 1. | Open "Start" -> "Programs" -> "Administrative Tools" -> "Services" and make sure that the service "SQLSERVERAGENT" is running and set to automatic start mode. |
| 2. | Open "SQL Server Enterprise Manager" and navigate to "SQL Server Group" -> "Your Servername" -> "Management" -> "SQL Server Agent" -> "Jobs": |
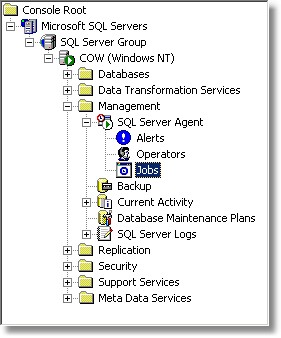
| 3. | Right-click "Jobs" in the left pane and select "New Job ..." |
| 4. | In the "General" tab, enter a name for the job, such as EventSentry Database Purge |
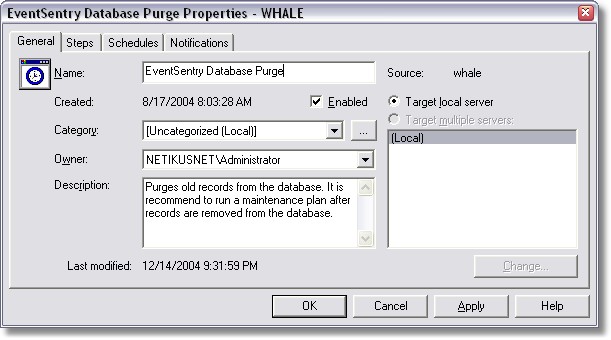
| 5. | Click on "Steps" and create a new step by clicking on the "New" button. In this step we will add a SQL script that deletes all records from the table that are older than 90 days. |
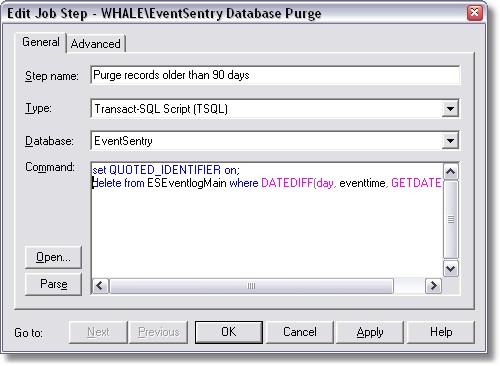
Apply a descriptive name to this step, set the type to "Transact-SQL Script", select the correct database and paste the following SQL command into the "Command" window:
set QUOTED_IDENTIFIER on;
delete from ESEventlogMain where DATEDIFF(day, eventtime, GETDATE()) > 90
where "EventSentry" is the name of the table and "90" are the number of days you want to keep records in the table. This script will remove all records from the table that are older than 90 days. Click OK to save this step.
Hint: To purge records from other tables as well simply repeat (5) and add another step, adapting the SQL script to reflect the new table name and field containing the time stamp. For the Process/Logon/Print Tracking, Diskspace and Environment table the script would look like this:
set QUOTED_IDENTIFIER on;
delete from ESPSTracking where DATEDIFF(day, start_datetime, GETDATE()) > 90
set QUOTED_IDENTIFIER on;
delete from ESDiskspace where DATEDIFF(day, recorddate, GETDATE()) > 90
set QUOTED_IDENTIFIER on;
delete from ESEnvironment where DATEDIFF(day, recorddate, GETDATE()) > 90
| 6. | Click on "Schedules" to specify how often you want to purge records. In our example we will purge records once a week, but you could also run this script daily or bi-monthly. Click on "New Schedule" and add a new recurring schedule. Assign a descriptive name to the schedule and click OK. |
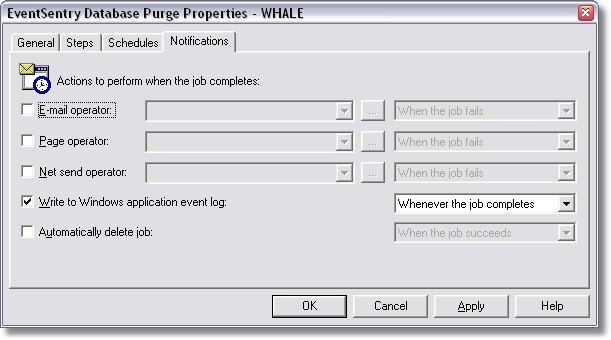
| 7. | At last you can specify whether you want to be notified when this job runs or generates an error. Click the "Notifications" tab and set the desired options. In our case we write an event to the event log every time the job runs: |
MySQL
MySQL does not currently ship with an equivalent of a SQL Server Agent where you would be able to schedule SQL commands. In order to run SQL commands on MySQL you can use a scripting language such as Perl for example, and you can then schedule your scripts using Windows' "Scheduled Tasks". Future versions of EventSentry will ship with an executable that will run SQL commands against a MySQL database.
In the meantime you can use the following SQL statements to purge records that are older than 90 days:
delete from ESEventlogMain where DATE_SUB(CURDATE(),INTERVAL 90 DAY) > eventtime
delete from ESPSTracking where DATE_SUB(CURDATE(),INTERVAL 90 DAY) > start_datetime
delete from ESDiskspace where DATE_SUB(CURDATE(),INTERVAL 90 DAY) > recorddate
delete from ESEnvironment where DATE_SUB(CURDATE(),INTERVAL 90 DAY) > recorddate
Oracle
Oracle does not currently ship with an equivalent of a SQL Server Agent where you would be able to schedule SQL commands. In order to run SQL commands on Oracle you can use a scripting language such as Perl for example, and you can then schedule your scripts using Windows' "Scheduled Tasks". Future versions of EventSentry will ship with an executable that will run SQL commands against a Oracle database.
delete from from ESEventlogMain where trunc(sysdate,'DAY') - eventtime + 1 > 90;
delete from from ESPSTracking where trunc(sysdate,'DAY') - eventtime + 1 > 90;
delete from from ESDiskspace where trunc(sysdate,'DAY') - eventtime + 1 > 90;
delete from from ESEnvironment where trunc(sysdate,'DAY') - eventtime + 1 > 90;