You can send event log records to remote Unix/Linux syslog servers either through the UDP or through the TCP protocol. Event log records are sent in the following format:
date time computername ID=Number:Eventlog:Event Type:Message
Example from an audit entry on a Linux host after it has been received from EventSentry:
Dec 11 09:33:24 blackjaguar ID=592:Security:AUDIT SUCCESS:A new process has been created: New Process ID: 3868 Image File Name: C:\winnt\system32\eventsentry_gui.exe Creator Process ID: 920 User Name: wizard Domain: BLACKJAGUAR Logon ID: (0x0,0xDB98) |
Carriage returns in the event log record will be removed automatically. The beginning of the syslog entry (date, time and computername in black) are generated by the syslog daemon and are not influenced by EventSentry.
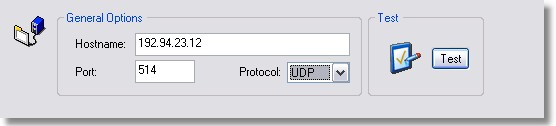
Hostname
The IP address or hostname of the remote syslog server.
Port
The port on which the remote syslog server is listening for incoming requests, 514 per default.
Protocol
The protocol to use, either UDP or TCP. Most hosts use the UDP protocol.
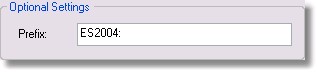
Optional Settings / Prefix:
You can have a text string prefix every syslog message that is sent out by EventSentry. Simply enter the string into the Prefix field.
Test
Send a syslog UDP message to the remote host
Most syslog daemons on Unix/Linux servers do not accept remote syslog packets by default. Please read the according manpages if you do not know how to enable this feature. On most Linux distributions you will need to pass the -x option to the syslog daemon upon startup. |